1. INTRODUCTION
• “If you have water, you can think of the future”.
• 22 March is celebrated as the world water day.
• The amount of water recommended by the United Nations for drinking, washing, cooking and maintaining proper hygiene is a minimum of 50 litres per person per day.
• This amount is about two and a half buckets of water per person per day.
• In some places there is an acute shortage of water. Taps running dry, long queues for water, fights, marches and protests for demand of water have become a common sight, especially during summers.
• Year 2003 was observed as the International Year of Freshwater to make people aware of this dwindling natural resource.
2. AVAILABILITY OF WATER
• Nearly 71% of the earth is covered by water in the form of oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, ice, ground water and moisture in the air. But most of it is not fit for human consumption.
• Water that is fit for human consumption is called freshwater. Only 0.006% of the water on the earth is actually available for our use.
3. FORMS OF WATER
In nature, water exists in three forms
• As a solid, it exists as icecaps at the poles, snow-covered mountains and glaciers.
• As a liquid, it is in the form of water in oceans, lakes and rivers, and underground water.
• Its gaseous form is the water vapor in the air around us.
4. WATER CYCLE OR HYDROLOGICAL CYCLE
The continuous cycling of water in nature that keeps the total amount of water on the earth constant is called water cycle.
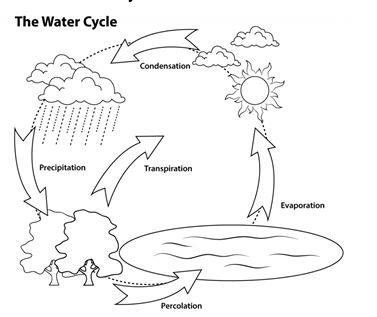
Processes involved in water cycle
The processes involved in the water cycle are, evaporation, condensation ,precipitation and infiltration.
(i) Evaporation
The process of conversion of water molecules into vapor is called evaporation. water vapor collects in the sky in the form of clouds.
(ii) Condensation
The process of conversion of water vapor into water by cooling is called condensation.
(iii) Precipitation
Water falls from the sky in the form of rain, snow, hail, or sleet, this process is called precipitation.
(iv) Infiltration
The process of seeping of water into the ground is known as infiltration.
(v) Aquifer
Sometimes, ground water accumulates between layers of hard rock. This is known as an aquifer. Water in aquifers can be drawn with tube wells and hand pumps.
5. WATER TABLE
The level below which the ground is saturated with water is called water table.
Ground water
Groundwater is the most important source of water for us. The water is stored under the ground; between layers of rocks. The upper limit of groundwater at a place is called the water table at that place. Water table is usually higher in the plains but is very low in the plateaus. This is the reason it is easier to install a hand-pump in the northern plains. On the other hand, it takes a heavy drilling machine to install a tube-well in the plateaus.
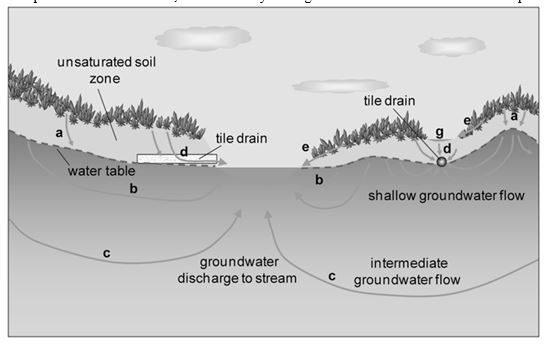
Depletion of water table
As long as the water drawn from the ground is replenished by seepage of rain water, the water table remains unaffected. The problem starts when we take more water from the ground than is replenished by natural means. Then the water table goes down, and it is said to have been depleted.
Reasons for depletion of the water table
• Increasing population that creates more demand for water.
• More wells are dug and water is drawn from them.
• Industrial activities are increasing the demand for water. For example, the construction industry uses tube wells to draw ground water.
• An increase in agricultural activities demands more water. In areas where there are no streams and lakes, ground water is used for irrigation.
• Scanty rainfall is another reason for depletion of the water table.
• Water table depletion can be a result of deforestation.
6. WATER MANAGEMENT
• Water managementis the continuous matching of water resources with the water requirements of a place.
• Water management essentially involves activities that identify sources of water, prevent wastage of water, and implement recycling of water.
• It may also include treatment of water to make it suitable for human consumption.
• Prevent wastage of water
• Water leaking from pipes Fixing Leaking taps.
• Water over-flowing from buckets while clothes are being washed alongside.
• Using water wisely while brushing the teeth, shaving, bathing, washing and during many other activities, practicing rainwater harvesting.
7. CONSERVATION OF WATER
Instead of letting rainwater runoff into the sea, it can be used to recharge ground water. This is known as rainwater harvesting.
Rainwater harvesting can be used to raise the water table in arid areas. It can also be used to create water storage areas.
Farming, which typically requires huge quantities of water, can also benefit from good water management.
Bawris
This is the old method of rain water storage and recharge. In olden days people built deep step wells into the ground. These deep step wells are called bawris. During rainy season these wells are filled with water. The water is stored in these wells for longer time because they are very deep the evaporation of water is less. During shortage people use this water.

Drip irrigation drip irrigation is an economical way of using water. This technique involves the use of tubes to deliver water straight to the base of a plant, where it is taken up by the roots.
8. EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY
Plants need water to absorb nutrients from the soil and make their food. Without water, plants would die, and greenery would be lost. This, in turn, would mean the end of all life on the earth, because without plants, there would be no food, oxygen or rainfall. There would also be many other problems.








