1. AIR
- Air is present everywhere on earth.
- We cannot see air, but we feel its presence in many ways.
- You notice it when the leaves of the trees rustle or the clothes hanging on a clothes-line sway. Pages of an open book begin fluttering when the fan is switched on. The moving air makes it possible for you to fly your kite.
- Winnowing is more effective in moving air.
- Air is present as a thick blanket surrounding the surface of the earth.
- The layer of gases around the earth is called as
- The atmosphere is dense at the surface of the earth and becomes thinner as one moves up.
Layers of Atmosphere
The atmosphere is divided into five layers. It is thickest near the surface and thins out with height until it eventually merges with space.
1. The troposphere is the first layer above the surface and contains half of the Earth’s atmosphere. Weather occurs in this layer.
2. Many jet aircrafts fly in the stratosphere because it is very stable. Also, the ozone layer absorbs harmful rays from the Sun.
3. Meteors or rock fragments burn up in the mesosphere.
4. The thermosphere is a layer with auroras. It is also where the space shuttle orbits.
5. The atmosphere merges into space in the extremely thin exosphere. This is the upper limit of our atmosphere.
2. IMPORTANCE OF AIR
- Air is essential for all living beings. It supports life on earth.
- Air is utilised by all the living organisms like plants, animals and microorganisms.
- Air cannot be seen but is felt when it moves.
- The movement of air is called breeze or wind depending on its velocity or speed.
- Air fills in the empty space available everywhere.
- We all breathe in air. Breathing is an essential part of respiration. We breathe in oxygen rich air and breathe out carbon dioxide rich air.
3. COMPONENTS OF AIR
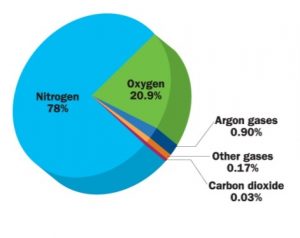
Air contains mostly nitrogen and oxygen. Nitrogen occupies 78% of the air. Oxygen occupies 21% of the air. 1% of the air is made up of carbon dioxide, other gases, water vapour, dust particles etc.
I. Nitrogen
- It is a lightest colourless, odourless gas. It generally occurs in its diatomic form N2.
- Nitrogen is used to control combustion.
- Nitrogen is used by plants and animals to synthesise proteins in the body.
- Nitrogen cannot be directly used by plants or animals. It has to be fixed into its nitrate or nitrite
- Nitrogen is used to manufacture fertilisers to increase soil fertility.
- Nitrogen is used to manufacture ammonia used for in many industries.
- Nitrogen oxidation of stored food in packets.
II. Oxygen
- It is a chemical element in the form of gas. Mostly it is diatomic, made up of two atoms. O2is the molecular oxygen.
- It is the active part of the air and one-fifth of total volume of air is oxygen.
- Oxygen is taken directly from the air by organisms living on land for respiration.
- Oxygen helps in oxidising the food eaten by organisms to release energy.
- Aquatic organisms take in oxygen dissolved in water.
- Oxygen is required for combustion and is used for welding purposes.
- Oxygen in the form of ozone helps in protection of living organisms from dangerous UV rays coming out from the sun.
- Liquid Oxygen is used as a fuel in rockets.
- Oxygen stored in the cylinders is used to provide artificial respiration to patients in the hospital. Oxygen mask is given to patient suffering from respiratory problems.
- Mountaineers, astronaut and sea divers carry oxygen cylinder with them but aeroplane passengers do not carry oxygen cylinder.
- Mountaineers carry Oxygen cylinder with them, while climbing mountains because air pressure is low at higher altitude.
Earthworms come out of the soil, only during heavy rains
Most of the small organisms like earth worms, rodents live inside the soil. They usually live in burrows and holes in the soil. These burrows also make spaces available for air to move in and out of the soil. However, when it rains heavily, water fills up all the spaces occupied by the air in the soil. In this situation, animals living in the soil have to come out for respiration.
III. Carbon Dioxide
- It is the gas which is made up of one carbon atom combining with two atoms of oxygen.
- Combustion of coal, fossil fuels and hydrocarbons, etc release carbon dioxide.
- CO2is used by plants in synthesising their food by the process of photosynthesis.
- CO2 is used in fire extinguishers.
- CO2 is used in storing soft drinks.
Note:
We feel suffocation in a room having burning substance due to accumulation of carbon dioxide gas and less availability of oxygen gas.
Activity to show presence of oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen in air:
For this, take a candle, a glass tumbler and a pan which is filled with some water. Keep the candle upright in the pan and light the candle. Now cover the candle with the glass tumbler. It is observed that the candle extinguishes after some time.
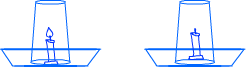
This happens because oxygen in the air inside the glass tumbler is utilised in burning the candle. All the oxygen gets converted into carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide does not support burning and hence candle stops burning.
Once the candle stops burning, some amount of water is sucked inside the tumbler. This happens because the volume of cabron dioxide is less than the volume of oxygen which was displaced.
It is also seen that a lot of air is still inside the tumbler. A major portion of this air is nothing but nitrogen. Nitrogen too does not support burning.
IV. Inert Gases
- These are also called as noble gases. They occupy a negligible percentage in air.
- Argon is used to fill the bulbs to prevent their filament.
- Helium is used in providing low temperatures.
- Neon is used to fill special bulbs called as neon signs.
- Radon is used in treating cancer patients.
V. Water Vapour
- It is a form of water present as gas in the air.
- Amount of water vapour in the air varies with sun’s heat.
- Hot sun can evaporate more amount of water and convert it into water vapour.
- It helps in the formation of clouds which later can come down as rain.Dust and Smoke
VI. Dust and Smoke
- Air contains some amount of dust and smoke in it.
- Tiny shining particles moving in beam of sunlight is dust particle in air moving in random
- Dust and smoke are contributed by vehicles and industries releasing them.
- These are harmful to human beings and can cause many respiratory diseases.
Note
- The burning of fossil fuels produce harmful smoke in atmosphere to cause air pollution.
- poisonous gas and dust particles are present in polluted air.
- Finer hairs inside the nose filter the dust particle while inhaling the air.
- In industrial area concentration of dust particle is more due to release of gas and dust particle from chimney of factories .
- The nose and mouth of traffic police at crossing is covered with mask due to presence of high pollutants in air.
4. OXYGEN-CARBON DIOXIDE LEVELS
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the air are maintained by different processes like respiration and photosynthesis.
- Respiration involves utilization of oxygen from air by living organisms and releasing carbon dioxide into air. It occurs in all living organisms.
- Photosynthesis involves utilization of carbon dioxide from air and release of oxygen into the air.
- Carbon dioxide is replenished by the process of respiration and oxygen is replenished by the process of photosynthesis.
5. PROPERTIES OF AIR
- Air is transparent. Air is a transparent medium which allows light to pass through it. The objects are seen clearly through air.
- Air is colourless. It is not visible.
- Air can be felt when it moves fast. Moving air is called as wind.
- Air occupies space. Air is present everywhere. Air can be displaced by water.
- Air exerts pressure.
- Air can be compressed and filled into a container.
6. AIR IS NECESSARY FOR COMBUSTION – ACTIVITY
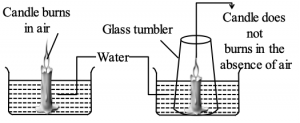
i) Take a glass trough and fill 1/3 of its volume with water.
ii) Add a spoonful of caustic soda (Sodium hydroxide) and few drops of coloured ink to the contents of the trough.
iii) Place a wooden slab or stone in the trough and place a lighted candle on it as shown in the figure.
iv) Invert a wide mouthed glass jar over the burning candle. The candle is put off within few seconds. At the same time the coloured water in the glass jar raises.
v) The supporter of combustion i.e., oxygen in the air, contained in the glass jar was exhausted and carbon dioxide is released in its Hence oxygen in the air is useful for combustion.
vi) The carbon dioxide so formed is absorbed by caustic soda solution. The nitrogen which is still available in air does not give support for burning.
vii) As vacuum is created in the glass jar, the coloured water raises in the trough.
viii) However if the glass jar is not placed in an inverted position over the burning candle, the candle goes on burning forever, as air is available continuously.
ix) Hence, we can say that oxygen in air is necessary for burning.
7. OTHER USES OF AIR
- Air is used to rotate wind mills, which can lift water.
- Wind energy is a renewable form of energy.
- Air is also used to rotate wind mills which can generate electrical energy by aerogenerators.
- Air is used in sail boats.
- Air helps in the scattering of seeds and pollens of plants. (pollination).
- Air helps in the movements of sailing yachts, gliders, parachutes and aeroplanes.








